The Canadian Space Agency recently had some of its experts working on the James Webb Space Telescope field some questions in a Reddit AMA ("ask me anything"). You can read the whole AMA here. Below are a few of the highlights.
How much better is Webb than Hubble?
Chris Willott: Webb is better than Hubble in many ways:
- Colder, so better in the infrared.
- Larger aperture, so better sensitivity and spatial resolution.
- Versatile science instruments with a range of observing modes allowing us to take images and spectra in new ways.
Neil Rowlands: Webb's near-infrared instruments (NIRCam, NIRSpec and NIRISS) will be (roughly) 100x more sensitive than any previous instrument / telescope combination. But the mid-infrared instrument MIRI is 10,000x more sensitive than any previous instrument at these wavelengths.
 |
| Comparing Webb and Hubble |
What is the coolest thing Webb is going to be used for?
Luminita Ilinca Ignat: Personally, I think it would be so cool to see the baby galaxies, a couple hundred million years after the Big Bang. It would be really awesome to see that far in time, and see how our world was born.
 |
| GOODS-S/ERS2 Field |
René Doyon: Detecting water in the atmosphere of habitable rocky planets. Finding water-worlds, like exoplanets completely covered by an ocean.
 |
| NASA’s Webb Will Seek Atmospheres around Potentially Habitable Exoplanets |
What potential discoveries excite you the most about the launch and use of the James Webb Space Telescope?
Neil Rowlands: JWST's near-infrared instruments (NIRCam, NIRSpec and NIRISS) will be (roughly) 100x more sensitive than any previous instrument / telescope combination. But the mid-infrared instrument MIRI is 10,000x more sensitive than any previous instrument at these wavelengths. Based on this I would guess that the most surprising discoveries, even completely new phenomena will be from MIRI. I can't wait to see the first MIRI images of the center of our galaxy.
 |
| The Infrared Milky Way |
What do you expect to learn about the galactic center of our Milky Way?
Chris Willott: The center of our galaxy contains a black hole with a mass of a few million times the mass of our Sun. Surrounding this are many stars and gas clouds whizzing around due to the black hole's gravity. With Webb we will be able to map out the type of stars (old or young) to understand how this region has evolved and also observe the flares of infrared emission that are caused by gas heated when falling towards the black hole.
 |
| Hubble-Spitzer colour mosaic of the galactic centre |
Is there a primary point of concern for the mission? Be it a stage of the launch or a delicate mechanism that could affect its success?
Neil Rowlands: For most of the deployments, there is some hope that, even if one or two elements fail, there will still be partial capability for valuable astronomical observations. The one single point-of-failure could potentially be the secondary mirror deployment. Without this effective deployment, light from the large primary mirror won't get to the science instruments, so, fingers crossed for that one.
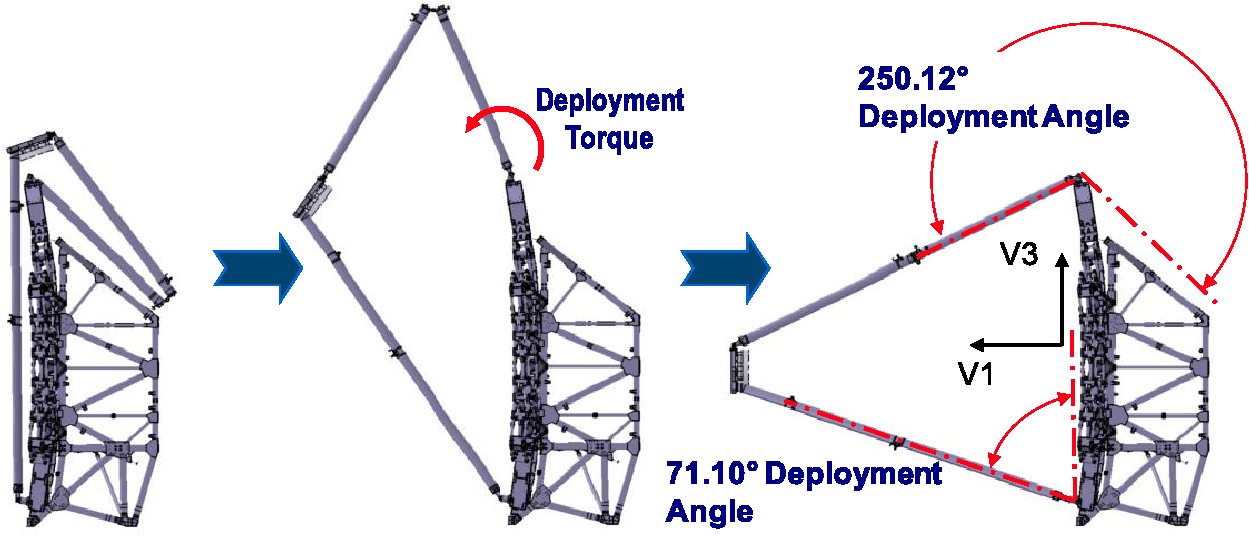 |
| The secondary mirror support structure deployment uses a simple four-bar linkage with a single driven hinge. |